Mastering Excel VBA Replace Character In String: The Ultimate Guide For 2023
Imagine this—you're knee-deep in an Excel project, and suddenly you realize that there are hundreds of unwanted characters scattered across your dataset. Panic sets in, but wait! Excel VBA to the rescue! Today, we’re diving deep into the world of Excel VBA Replace Character in String. This powerful technique will change the way you handle messy data forever. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced user, this guide has got you covered. So, buckle up, and let’s get started!
Excel VBA is like a superpower for anyone who works with spreadsheets. It allows you to automate repetitive tasks, clean up data, and even replace characters in strings with just a few lines of code. In this article, we’ll explore how you can harness the power of VBA to replace unwanted characters in your strings. Trust me, once you master this skill, you’ll wonder how you ever lived without it.
But before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let me tell you why this is such a game-changer. Let’s say you’ve got a massive dataset with inconsistent formatting—extra spaces, weird symbols, or incorrect characters. Cleaning it manually would take forever. Enter VBA Replace Character in String, your new best friend in the world of data wrangling.
Read also:What It Do Dave The Ultimate Guide To Understanding His Rise Influence And Legacy
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Excel VBA Replace Character in String
- Understanding the Basics of VBA
- The Syntax of Replace Function in VBA
- Practical Examples of Using Replace in VBA
- Biography of the Replace Function
- Advantages of Using VBA for String Manipulation
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Pro Tips for Mastering VBA Replace
- Real-World Applications of VBA Replace
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Excel VBA Replace Character in String
What is Excel VBA?
Excel VBA, or Visual Basic for Applications, is like the secret weapon hiding inside Excel. It’s a programming language that lets you automate tasks, create custom functions, and manipulate data in ways that would take hours if done manually. Think of it as the turbo boost for your spreadsheet skills.
Why Use VBA for Replacing Characters?
Replacing characters in strings might sound simple, but when you’re dealing with thousands of rows of data, simplicity turns into chaos. VBA offers a streamlined approach to tackle this problem. With just a few lines of code, you can replace any character in a string, clean up your data, and save yourself tons of time.
Let’s say you have a column full of phone numbers, but some of them have dashes, parentheses, or spaces. Manually editing each one would drive anyone insane. But with VBA, you can replace all those pesky characters with just a few clicks. Cool, right?
Understanding the Basics of VBA
Getting Started with VBA
Before we jump into replacing characters, let’s talk about the basics. First, you need to enable the Developer tab in Excel. Trust me, it’s worth the effort. Once you’ve got that set up, you can access the VBA editor by clicking on “Visual Basic” in the Developer tab.
Inside the VBA editor, you’ll see a blank slate where you can start writing your code. Don’t worry if it looks intimidating at first. By the end of this guide, you’ll be writing VBA code like a pro.
Key Components of VBA
- Macros: These are recorded actions that you can replay with a single click.
- Modules: Think of these as containers for your VBA code. You write your scripts inside modules.
- Functions: These are reusable pieces of code that perform specific tasks. We’ll be using the Replace function a lot in this guide.
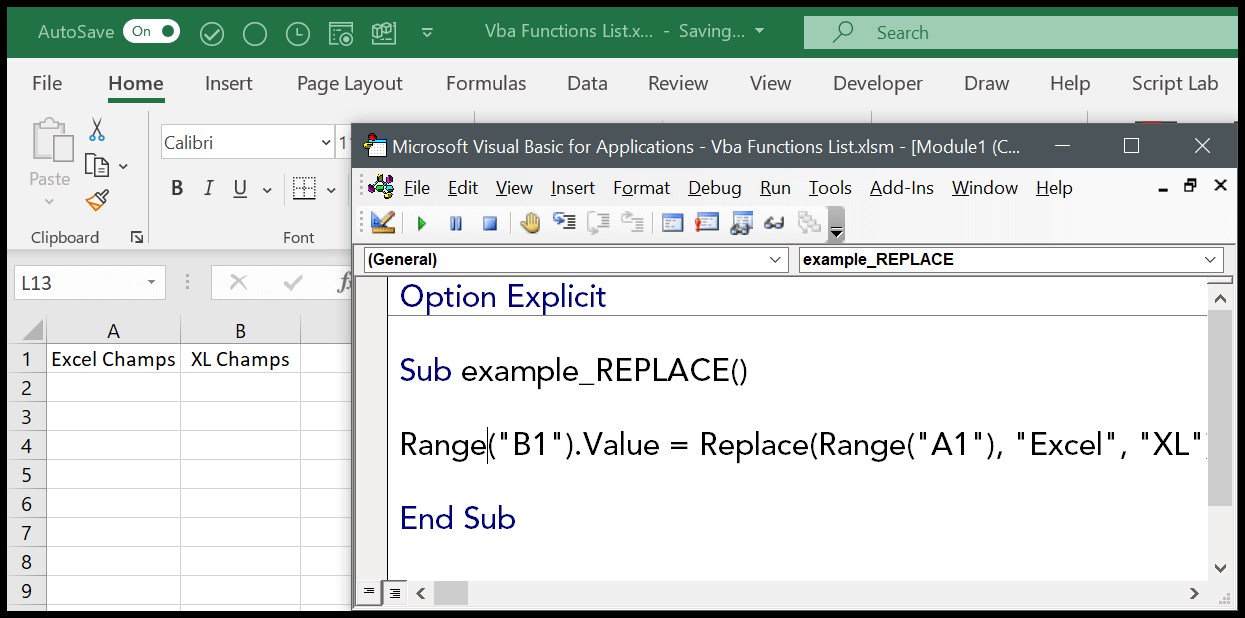
The Syntax of Replace Function in VBA
Now, let’s talk about the star of the show—the Replace function. The syntax is pretty straightforward:
Read also:Famous Birthdays On March 14th Celebrating The Lives Of Icons Who Mark This Special Day
Replace(expression, find, replace[, start[, count[, compare]]])
Let’s break it down:
- Expression: This is the string you want to modify.
- Find: The character or substring you want to replace.
- Replace: The new character or substring that will replace the old one.
- Start: Optional. The position in the string where the replacement should start.
- Count: Optional. The number of replacements to make.
- Compare: Optional. Specifies the type of comparison (e.g., case-sensitive or not).
For example, if you want to replace all spaces in a string with underscores, your code might look like this:
myString = Replace(myString, " ", "_")
Practical Examples of Using Replace in VBA
Example 1: Cleaning Phone Numbers
Let’s say you have a column of phone numbers with inconsistent formatting. Some have dashes, others have parentheses, and some even have spaces. Here’s how you can clean them up:
Dim phoneNumber As String
phoneNumber = Replace(phoneNumber, "(", "")
phoneNumber = Replace(phoneNumber, ")", "")
phoneNumber = Replace(phoneNumber, "-", "")
phoneNumber = Replace(phoneNumber, " ", "")
This code will remove all unwanted characters, leaving you with a clean phone number.
Example 2: Replacing Special Characters
Special characters can wreak havoc on your data. Let’s say you want to replace all @ symbols with the word “at”:
Dim email As String
email = Replace(email, "@", "at")
Simple, right? Now your emails are safe from any system that doesn’t like special characters.
Biography of the Replace Function
| Function Name | Replace |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Replaces characters in a string |
| First Appearance | VBA Version 1.0 |
| Popularity | Highly popular among data analysts and VBA enthusiasts |
The Replace function has been a staple in VBA since its early days. Its simplicity and effectiveness have made it a favorite among programmers and data analysts alike. Whether you’re replacing a single character or an entire substring, Replace is your go-to function.
Advantages of Using VBA for String Manipulation
1. Time-Saving
Manual data cleaning can be a nightmare. With VBA, you can automate the process and save yourself hours of work. Who wouldn’t want that?
2. Consistency
When you use VBA to replace characters, you ensure that the changes are applied consistently across your entire dataset. No more worrying about missed edits or inconsistencies.
3. Scalability
VBA scripts can handle large datasets with ease. Whether you’re working with a few rows or a million, VBA can scale to meet your needs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even the best VBA programmers make mistakes sometimes. Here are a few common ones to watch out for:
- Forgetting to Save Your Work: Always save your VBA code before running it. Trust me, you don’t want to lose hours of work because of a simple oversight.
- Not Testing Your Code: Before running your code on a large dataset, test it on a small sample to make sure it works as expected.
- Ignoring Error Handling: Errors happen, and it’s important to handle them gracefully. Use On Error statements to catch and deal with unexpected issues.
Pro Tips for Mastering VBA Replace
Here are a few tips to help you become a VBA Replace master:
- Use Variables: Always use variables to store your strings. It makes your code cleaner and easier to read.
- Comment Your Code: Comments are your friend. They help you remember what your code does and make it easier for others to understand.
- Practice Regularly: Like any skill, mastering VBA takes practice. Spend a little time each day writing and testing your code.
Real-World Applications of VBA Replace
VBA Replace isn’t just for cleaning up phone numbers and emails. Here are a few real-world applications:
- Data Cleaning: Remove unwanted characters from large datasets.
- Text Formatting: Convert text to uppercase, lowercase, or proper case with ease.
- Automation: Automate repetitive tasks that involve string manipulation.
Whether you’re a data analyst, a financial analyst, or just someone who loves spreadsheets, VBA Replace can make your life easier.
Conclusion and Next Steps
We’ve covered a lot of ground in this guide, from the basics of VBA to advanced techniques for replacing characters in strings. By now, you should have a solid understanding of how to use VBA Replace to clean up your data and automate repetitive tasks.
So, what’s next? Keep practicing, keep exploring, and most importantly, keep learning. The world of VBA is vast and full of possibilities. Who knows, you might just discover your next favorite function.
And don’t forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues. Knowledge is power, and the more people who know about VBA Replace, the better. Happy coding!
Article Recommendations